Introduction
The quintessential failure mode of continual learning is catastrophic forgetting, in which new knowledge supplants old knowledge, resulting in high plasticity but little stability. To deal with such forgetting, Rolnick et al. propose a simple technique, Continual Learning with Experience And Replay(CLEAR), mixing on-policy learning from novel experiences (for plasticity) and off-policy learning from replay experiences (for stability). For additional stability, they introduce behavioral cloning between the current policy and its past self.
CLEAR
CLEAR uses IMPALA with an experience replay. For the replayed experiences, two additional losses are added to induce behavior cloning between the network and its past self. Specifically, they penalize 1) the KL divergence between the historical policy distribution and the present distribution, and 2) the L2 norm of the difference between the historical and present value functions
\[\begin{align} \mathcal L_{policy-cloning}&=\sum_a\mu(a|h)\log{\mu(a|h)\over \pi_\theta(a|h)}\\\ \mathcal L_{value-cloning}&={1\over 2}\Vert V_\theta(h)-V_{replay}(h)\Vert_2^2\\\ \mathcal L&=\mathcal L_{IMPALA}+\lambda_v\mathcal L_{value-cloning}+\lambda_{p}\mathcal L_{policy-cloning} \end{align}\]Where \(h\) is the hidden state, \(\lambda_v=\lambda_p=.01\) .
Experiments
Rolnick et al. consider three distinct tasks within DMLab environments, and compare three training paradigms:
- Training networks on individual tasks separately
- Training a network on all tasks simultaneously
- Training a network sequentially from one task to another, and so on cyclically
They observe that in DMLab, there is very little difference between separate(1) and simultaneous(2) training. In fact, simultaneous training performs marginally better than separate training, indicating there is slight constructive interference.
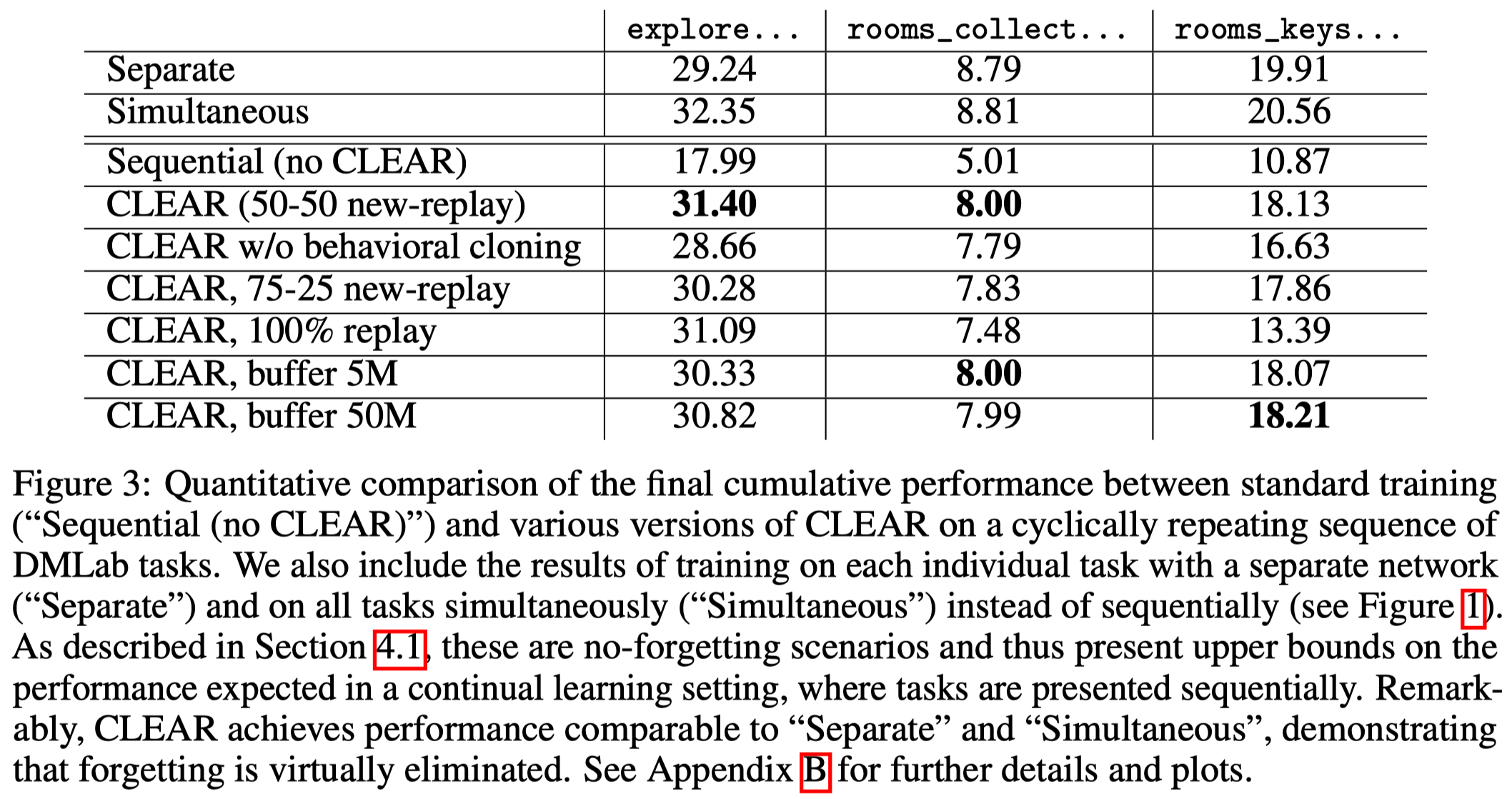
Figure 3 shows that CLEAR significantly helps mitigate the effect of catastrophic forgetting. In fact, in DMLab, CLEAR achieves performance comparable to separate and simultaneous training.
References
Rolnick, David, Jonathan Schwarz, Timothy P Lillicrap, and Greg Wayne. 2019. “Experience Replay for Continual Learning,” no. NeurIPS.

