Introduction
We discuss a general-purpose conditioning method for neural networks called Feature-wise Linear Modulation(FiLM), proposed by Perez et al. 2017
Method
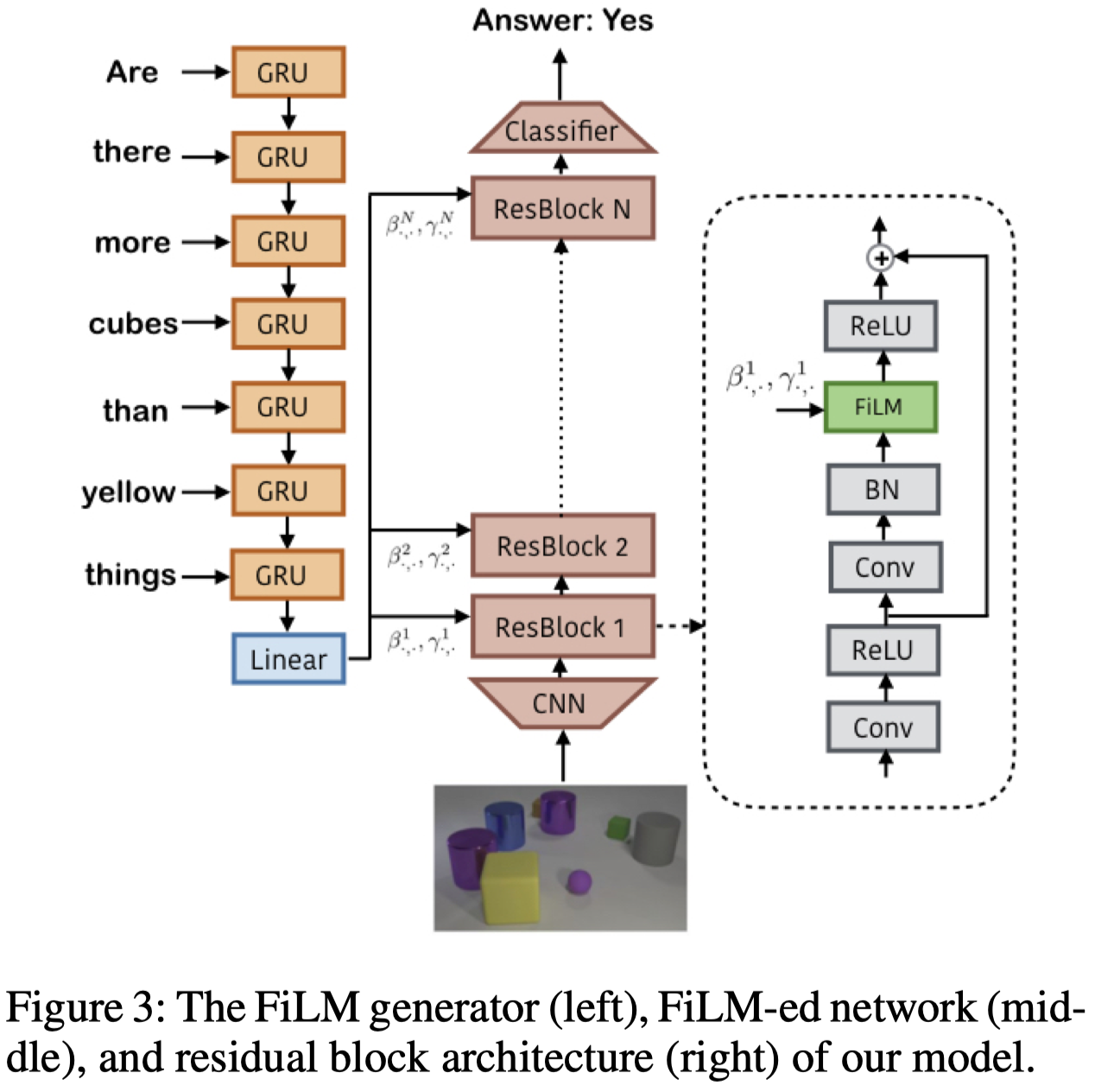
FiLM conditions the image on a query embedding, which is usually given by an RNN(e.g., GRU) output. Concretely, FiLM takes the RNN output and transforms it through a linear model, producing \((\pmb \beta^i,\pmb \gamma^i)\) vector for the \(i^{th}\) ResBlock. \((\pmb \beta^i, \pmb \gamma^i)\) modulate the activation by scaling and shifting each feature map:
\[\begin{align} \pmb y^i=\pmb \gamma^i\pmb x^i+\pmb\beta^i \end{align}\]Notice that we do not put any constraints on \(\pmb \gamma\) and \(\pmb\beta\). Ablations show this unconstrained version performs best.
Experimental Results

Figure4 shows FiLM succeeds in capturing the features of areas near answer-related or question-related objects.
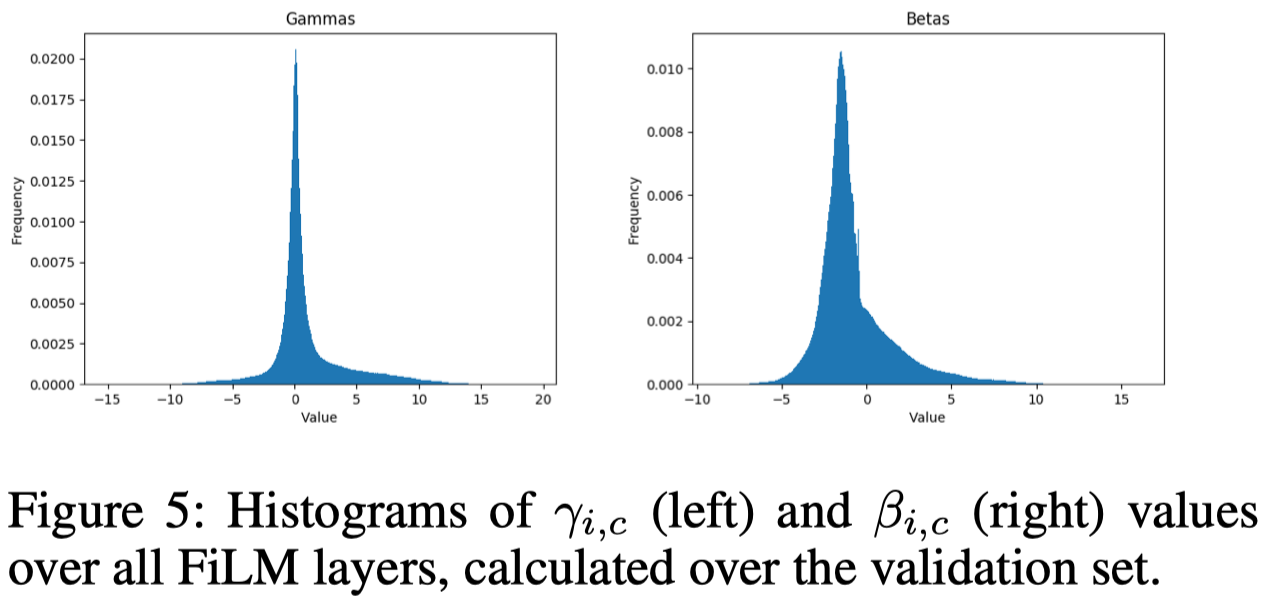
To analyze at a lower level how FiLM uses the question to condition the visual pipeline, we plot \(\gamma\) and \(\beta\) values predicted over the validation set. As shown in Figure 5, \(\gamma\) values show a sharp peak at \(0\), suggesting that FiLM learns to use the question to shut off or significantly suppress whole feature maps. Furthermore, a large fraction (\(36\%\)) of \(\gamma\) values are negative; since the model uses a ReLU after FiLM, \(\gamma <0\) can cause a significantly different set of activations to pass the ReLU to downstream layers than \(\gamma>0\).
Perez et al. 2017 also present a set of interesting ablations, showing that FiLM obtains a general performance gain across a variety of different architectures.
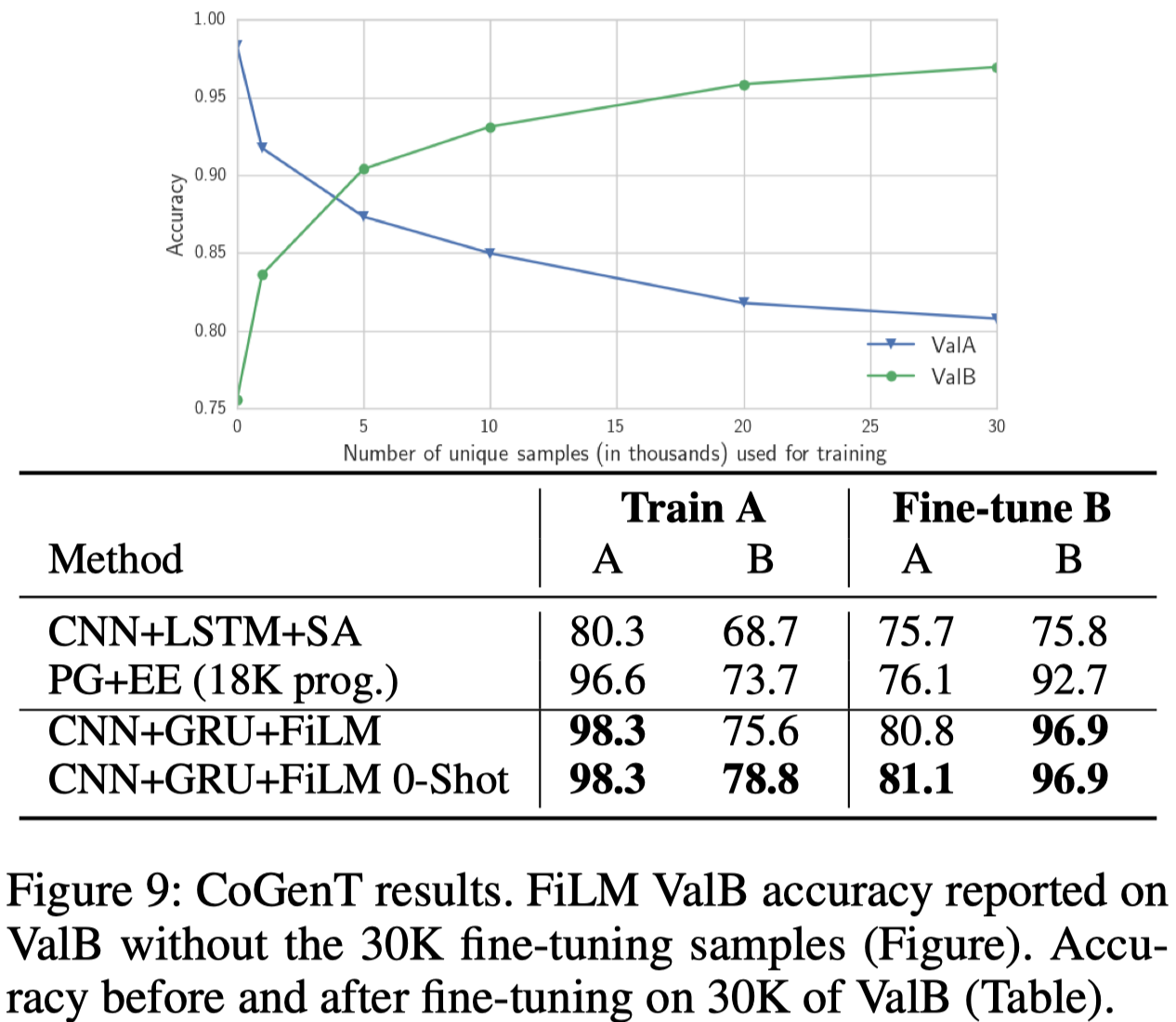
Experiments show that FiLM achieves SOTA(2017) performance on visual reasoning task. Moreover, Figure 9 shows that, when fine-tuning for a new dataset, FiLM achieves prior SOTA accuracy with 1/3 as much fine-tuning data. The bad news is it still suffers from catastrophic forgetting after fine-tuning.
References
Perez, Ethan, Florian Strub, Harm De Vries, Vincent Dumoulin, and Aaron Courville. 2017. “FiLM : Visual Reasoning with a General Conditioning Layer.”
Code: https://github.com/ethanjperez/film

